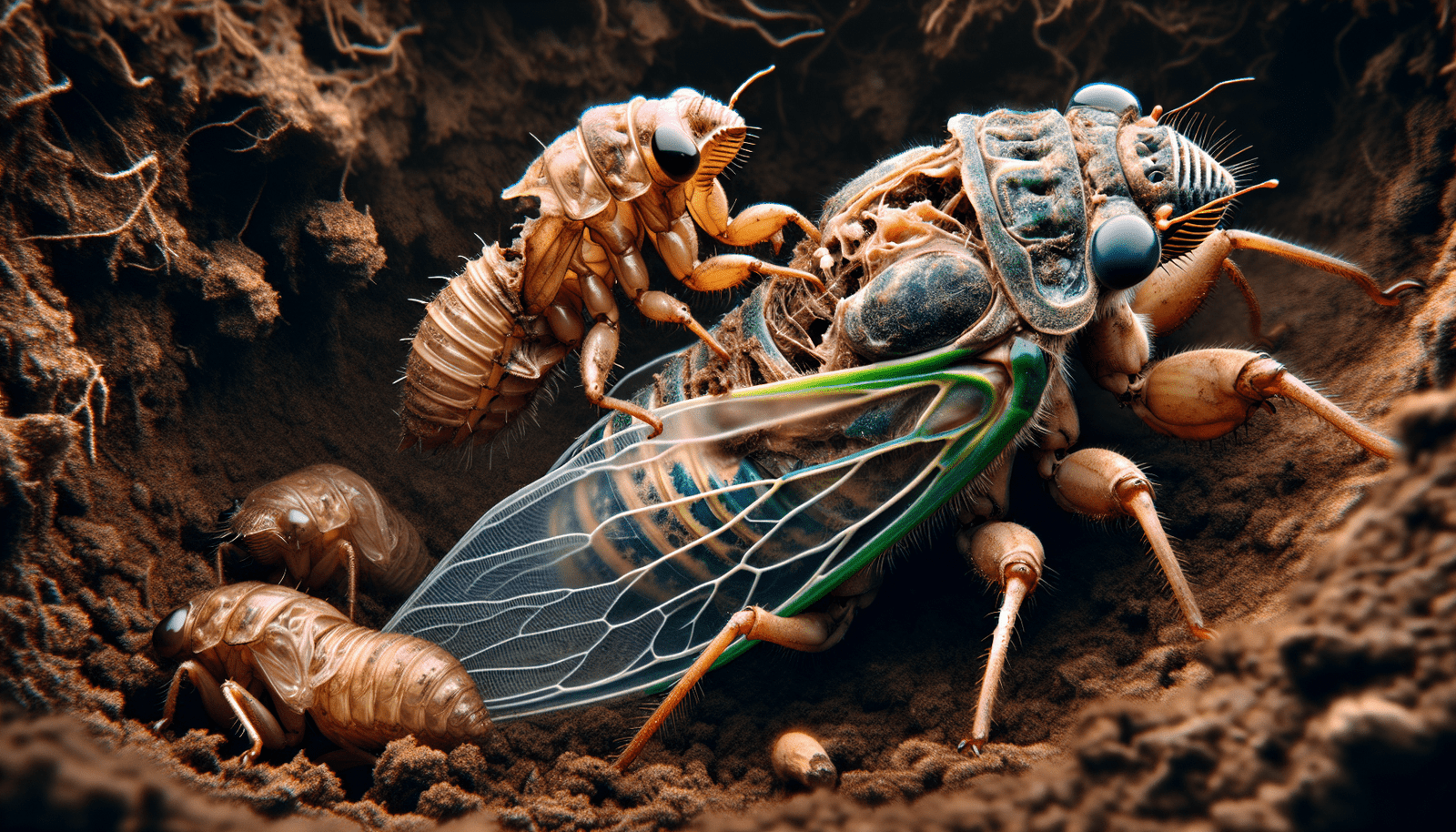
Welcome to a fascinating journey into the world of cicada nymphs! In this article, we will explore the early stage of their lifecycle and delve into the intriguing details of these unique creatures. From their underground habitat to their molting process, you will gain a deeper understanding of how cicada nymphs navigate the world before emerging as the loud and colorful insects we are more familiar with. Get ready to be amazed by the wonders of nature as we uncover the secrets of these fascinating creatures.
Understanding Cicada Nymphs: The Early Stage Of Their Lifecycle
Have you ever wondered about the fascinating world of cicadas? Specifically, have you ever been curious about the early stages of their lifecycle as nymphs? In this article, we will delve into the intricate details of cicada nymphs, shedding light on their development, behavior, and significance in the ecosystem. So, sit back, relax, and let’s explore the enchanting world of cicada nymphs together!
What Are Cicada Nymphs?
Cicada nymphs are the immature stages of cicadas that hatch from eggs laid by adult female cicadas. These nymphs are wingless and live underground, feeding on the sap of plant roots for several years before emerging as adults. They undergo a series of molts as they grow and develop, shedding their exoskeleton to accommodate their increasing size.
Cicada nymphs are an essential part of the cicada life cycle, playing a crucial role in the population dynamics and survival of the species. As they feed on plant roots, they contribute to nutrient recycling and soil aeration, benefiting the ecosystem in which they reside.
Lifecycle of Cicada Nymphs
The lifecycle of cicada nymphs can vary depending on the species, with some spending as little as two years underground and others remaining there for up to 17 years. These extended periods of underground development are unique to cicadas and are one of the defining characteristics of this fascinating insect.
During their time underground, cicada nymphs go through five instars, or developmental stages, marked by molting and growth. Each instar is a critical phase in the nymph’s development, enabling it to increase in size and prepare for its eventual emergence as an adult cicada.
As cicada nymphs feed on plant sap, they grow and mature, undergoing molting to shed their exoskeleton and accommodate their expanding bodies. This process is repeated several times throughout their time underground, with each molt marking a transition to a new instar.
Behavior of Cicada Nymphs
Cicada nymphs exhibit fascinating behaviors as they navigate their underground world, seeking food, avoiding predators, and preparing for their emergence as adults. These behaviors are crucial for their survival and play a significant role in shaping the population dynamics of cicadas.
One of the most remarkable behaviors of cicada nymphs is their feeding on the sap of plant roots. This feeding behavior provides essential nutrients for the nymphs’ growth and development, enabling them to mature and prepare for their eventual emergence.
Another important behavior of cicada nymphs is their sensitivity to environmental cues that signal the timing of their emergence. Factors such as temperature, soil moisture, and day length play a role in triggering the emergence of adult cicadas from their underground habitat.
Significance of Cicada Nymphs in the Ecosystem
Cicada nymphs are essential components of the ecosystem, contributing in various ways to the functioning and balance of natural systems. Their feeding on plant roots helps to recycle nutrients and promote soil health, benefiting the plants and other organisms in their environment.
As cicada nymphs molt and grow underground, they also aerate the soil, creating channels and pathways for water, air, and nutrients to reach plant roots. This soil aeration is critical for plant growth and health, enhancing the overall productivity and resilience of the ecosystem.
Furthermore, cicada nymphs serve as a food source for a variety of predators, including birds, mammals, and other insects. By providing a valuable food resource for these predators, cicada nymphs contribute to the biodiversity and stability of the food web in which they are a part.
Differences Between Periodical and Annual Cicada Nymphs
There are two main types of cicadas based on their lifecycle patterns: periodical cicadas and annual cicadas. These two groups differ in their development, emergence patterns, and behaviors, reflecting unique adaptations to their respective environments.
Periodical cicada nymphs, as the name suggests, have an extended developmental period underground, with some species remaining there for up to 17 years. These cicadas emerge in synchronized mass emergences, overwhelming predators and maximizing their chances of survival and reproduction.
In contrast, annual cicada nymphs have shorter developmental periods underground, with some species completing their lifecycle in as little as two years. These cicadas emerge on an annual basis, with smaller, more scattered emergences compared to periodical cicadas.
The differences between periodical and annual cicada nymphs highlight the diverse strategies that cicadas have evolved to cope with their environment and maximize their reproductive success. By understanding these differences, we can gain insight into the complex adaptations of cicadas and their significance in the ecosystem.
Observing Cicada Nymphs in the Wild
If you are interested in observing cicada nymphs in their natural habitat, there are a few key tips to keep in mind to enhance your chances of a successful encounter. First and foremost, it is essential to research the species of cicada that are native to your area and their typical emergence patterns.
Once you have identified the species of cicada you are interested in observing, you can begin to search for nymphs in suitable habitats, such as wooded areas, forests, or grasslands. Look for signs of nymph activity, such as exit holes in the ground or discarded exoskeletons from molting.
During your search for cicada nymphs, be patient and observant, as these insects can be elusive and may require time and effort to locate. Bring along a field guide or reference materials to help you identify the nymphs you encounter and learn more about their behavior and ecology.
By approaching your observation of cicada nymphs with curiosity, respect, and a willingness to learn, you can gain a deeper appreciation for these fascinating insects and the vital role they play in the ecosystem. So, grab your binoculars, pack a notebook, and head out into nature to explore the enchanting world of cicada nymphs!
Conclusion
In conclusion, cicada nymphs are a captivating and essential part of the cicada lifecycle, undergoing a series of molts and growth stages underground before emerging as adult cicadas. Their behaviors, development, and significance in the ecosystem highlight the intricate connections between insects and their environment, shaping the biodiversity and functioning of natural systems.
By understanding the lifecycle of cicada nymphs, we can gain insights into the fascinating adaptations and strategies that these insects have evolved to survive and thrive in their habitats. Whether you are a seasoned entomologist or a curious nature enthusiast, exploring the world of cicada nymphs can be a rewarding and enriching experience, deepening your appreciation for the wonders of the natural world. So, the next time you hear the buzz of cicadas in the trees, take a moment to ponder the remarkable journey of these insects from nymphs to adults, and marvel at the intricate dance of life unfolding all around us.